Research - (2023) Volume 18, Issue 6
IMPACT OF CURRICULUM STANDARDS SIX SIGMA IN IMPROVING THE QUALITY OF BANKING SERVICE: AN APPLIED STUDY OF A SAMPLE OF ISLAMIC BANKS IN IRAQ
Hayder Ali Kadhim Alfatlawi1* and Wasan Khifah Abdulridha Alsaedi2*Correspondence: Hayder Ali Kadhim Alfatlawi, Lecturer at Al-Tuff College University, Iraq; Candidate student at University of Karabuk (UNIKA), Turkey, Email:
Abstract
The research aimed to demonstrate the effect of using curriculum standards Six Sigma The dimensions combined (senior Leadership support, Feedback And measurement, continuous Improvement, Processes And systems, Human Resources) to improve quality service banking in Islamic banks in Iraq. To achieve the objectives of the study, a questionnaire was designed through Google Forms consisting of (48) items to collect primary data from the random study sample. The respondents were (39) individuals working in Iraqi Islamic banks. In light of this, data was collected and analyzed, and hypotheses were tested using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) program. V.23 and many statistical methods to achieve the objectives of the study and reach its results, including multiple linear regression analysis. The study reached several results, the most important of which is that there is a statistically significant impact of the standards of the Six Sigma approach with its combined dimensions in improving the quality of banking services in Iraqi Islamic banks at a significant level of 0.05. There is a direct, statistically significant correlation between the standards of the Six Sigma approach with its combined dimensions and the quality of banking service The level of significance is 0.05, and in light of the results of the study, the researcher recommended several recommendations, the most important of which are encouraging banks to use financial analysis as a control method to quickly detect errors and deviations, developing and strengthening security procedures to protect customer naccounts and personal information by providing additional verification techniques such as identification. Face and fingerprint to increase security, work on training and developing employees through workshops to ensure that they are familiar with all naspects of advanced banking services and encourage them to provide distinguished and exceptional customer service that meets their needs and requirements.
Keywords
Curriculum Six Sigma. Banking service quality. Islamic banks. Iraq
Introduction
Organizations in our world today face many challenges, perhaps the most prominent of which is the growing intensity of competition in light of the widespread global markets, technology, and economic blocs. Therefore, most of these organizations have tended to pay attention to the quality of what they provide to their customers,specifically the quality of banking service and its measurement (Bonnie& Naima, 2016(.The development of comprehensive quality management was initiated and new advanced and modern methods and techniques were found to reduce errors, including the Six Sigma method, which is a method that helps organizations reach a high level of accuracy and quality degrees using statistical tools and techniques (Bovas, 2013). Motorola was the first company to develop Six Sigma was developed in the 1980s as a result of the recognition that products with a high first return rarely fail in use and is a statistical term that dates back to the 19th century (Krishnan, & Prasath, 2013). Although many proponents of Six Sigma stress the uniqueness of this approach, It is part of the continuing evolution of thinking about what might broadly be called "quality" (Knowles, 2011). Because Six Sigma management is a quality management method that has recently been adopted by many company leaders, it is a data-driven, customer-focused method that leads companies to reach the best level of quality (Lee, & Choi, 2006). The finance industry has widely applied Six Sigma to the quality process to eliminate defects. With the most famous companies and banks in the world sharing knowledge and lessons related to implementing Six Sigma and talking about the savings and improvements they have made (Flayyih & Khiari, 2023; Maseer et al., 2022). However, the process model has only been used sometimes (Stoiljkovic et al., 2010). So Six Sigma is not just a qualitative initiative, But a business initiative is more valuable to financial institutions now than it has ever been, and companies are now reaping real savings and revenue growth (Uprety, 2009). That is why Six Sigma is not only viewed as a statistical tool but also as a perspective for business strategy (Antony & Banuelas,2002). By reducing customer operating costs and cycles while improving customer satisfaction under a management model that enhances the organization's profitability to improve the quality of its operations, that is, as an effective management strategy for companies and banks to obtain competitiveness and sustainable development in a new economic environment (Zhuo, 2019). It also represents a tool for improving and developing processes based on customer feedback and opinions, data collection, and analysis techniques to lead and keep pace with the improvement process, that is, processes that do not result in more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities, or the absence of defects, or that they are almost zero (Garrison, et.al., 2010). It is mainly based on the DMAIC cycle) definition: setting goals based on VOCs )voice or expectations of the customer), measurement: measuring the actual performance of the process, collecting data and determining key characteristics and parameters, analysis: analyzing the collected data to determine the causes of the problem that are likely to affect Imperfections Stabilize the process, Optimization: finding and implementing the solution to problems identified as a result of selecting and selecting the most valuable problem to apply to reduce process variability, Control: ensuring continuous monitoring of the process; successful improvements must be standardized as a basis for further actions (Kowalik, 2018). This is why the Six Sigma method deserves special attention due to the importance of service quality being an increasingly valid aspect of business for companies that aspire to achieve market success in an environment characterized by high competition and instability. Service quality has been included in many different theoretical and practical studies, one of them being practical executive probability(Abass et al., 2023; Ali et al., 2023). To improve production (methods and tools) on the service side (Uluskan, 2016). Intense competition has been recognized as the key to maintaining excellent profit and a reliable link to achieve customer satisfaction (Hassoun, & Khalaf, 2022). As for the banking sector, it represents one of the most vital 65 economic sectors because it deals with a broad base of clients and customers. It has been influenced by the development that has occurred in the field of banking services, so it has contributed to the implementation of new mechanisms that are flexible and facilitate mutual dealings between clients and customers.
And banking management (Basri, & Taher, 2018). The problem of the study was that Represented Banking service and its quality in the Iraqi sector was affected by weakness due to Iraqi banks continuing to use traditional methods of banking and not shifting towards using electronic banking techniques, which led to a lack of customers and a decrease in the customer base and thus a lack of profits. (Basri, & Taher, 2018). The stifling economic crisis that struck the country led to a decline in the level of performance of all businesses and organizations in the Iraqi economy (Al-Rubaye, 2020). It faced many problems and variables as a result of the nature and specificity of the environmental conditions in which it carries out its activities, which made it vulnerable to a common problem, which is Iraqi banks’ weak awareness of the importance of the dimensions of banking service quality (Kateh & Muhaisen, 2022). The weakness of the organizational and administrative structures, in addition to the narrowness of the administrative systems and the lack of sufficient flexibility and flow within the organization, is reflected in the bank's performance levels and the quality of its services (Bushra & Acer, 2017). Efforts are being made by Iraqi banks to improve the quality of their services, and now there is a noticeable decrease in the level of quality of service provided (Alabboodi, 2019). This requires that more attention be given to it by the Iraqi banking sector (Elias & Azhar, 2019). Because most Iraqi banks are close to traditional banks in terms of addressing many organizational problems, which makes they need to make radical changes towards correcting paths by adopting advanced administrative approaches, and one of these approaches is adopting the dimensions of the quality of banking service in... Evaluating its services and improving their quality within the framework of the organizational integration, it achieves (Acer, 2022). Due to the weakness in the quality of banking service in the Iraqi banking sector and to improve it to keep pace with global developments to gain customer satisfaction and expand the customer base, curriculum standards were taken. Six Sigma to demonstrate the impact on improving the quality of banking service. Therefore, the problem of the study can be formulated with the following main question: What is the impact of the standards of the Six Sigma approach on improving the quality of banking service for a sample of Islamic banks in Iraq? The main objectives of the research were to clarify the criteria for the curriculum Six Sigma, and Six Sigma practices in the banking sector, and a statement of the impact of the standards of the Six Sigma approach in improving the quality of banking service for a sample of Islamic banks operating in Iraq. It represents the main objective of the research and will be answered by analyzing the opinions of the respondents. The research objectives are crystallized by the research questions. Q1. What are the standards of the Six Sigma approach? Q2. What are Six Sigma practices in the banking sector? Q3. What is the impact of the Six Sigma standards on improving the quality of banking service for a sample of Islamic banks in Iraq? The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Section Two, a review of relevant previous studies and theoretical framework, Section Three: methodology, data, and analysis of respondents' opinions, Section Four: Conclusions and recommendations.
Review previous studies and theoretical framework
Previous studies
Insert (Salaheldin & Abdelwahab, 2009) Some of the advantages obtained by financial institutions as a result of implementing Six Sigma, such as what occurred in City Bank and JP Morgan for global investment banking services, the most important of which are a reduction in internal callbacks by 80%, external callbacks by 85%, and credit processing time. By 50%, reducing the cycle time for customers who submit service requests to the credit decisionmaking department by 67%, that is, from 3 days to 1 day, reducing the cycle time from 28 to 15 days, increasing customer satisfaction, and improving stability and cycle time by more than 30%. It is expected to be Six Sigma developed a program to improve quality by reducing process variability to the point where there are only 3.4 unacceptable defects per million process orders through the use of DMAIC and DMADV improvement strategies in addition to deploying a structured set of quality tools (Kumar et al., 2008). Most importantly, it has evolved Six Sigma is a powerful management strategy with its original goal of fewer than four defect failures or errors per million opportunities to include a wide range of approaches to integrating quality into products and services at the innovative design and development stages and throughout their lifespan (Cheng, 2008). More importantly, Rose (Chakrabarty & Chuan Tan, 2007) investigated many articles related to Six Sigma in services and filtered their results. They firmly believed that Six Sigma is a modern improvement initiative that is difficult to implement in services because the service process cannot be easily modified, but they highlighted the success factors for implementing Six. sigma is used in all manufacturing and service sectors such as commitment to senior management, education and training, cultural change, customer focus, clear performance metrics, attaching financial benefit to success and a structured understanding of the business process. On the contrary, the study (Hensley & Dobie, 2005) study dealt with effective identification to prove the readiness of Six Sigma to face the difficulties of the services provided. The difficulties were identified, and their forms were explained, as they were represented by measuring customer satisfaction, collecting data, and measuring sub-data. Pointed out (Dinell, 2003) Six Sigma is It is an effective model that works to help bankers, especially at Bank of America, by working to identify invisible errors within the bank to enable those in charge of identifying and diagnosing gaps to address them. Also, the availability of application requirements Six Sigma explains 0.69% of the variance in applying the Six Sigma methodology (DMAIC) and applying the Six Sigma (DMAIC) method explains 0.48% of Difference in the quality of health services performance in those institutions (Hammam & Ashraf, 2012). (Khaled,2014) included that commercial banks in Palestine use an approach Six Sigma in rationalizing investment decision-making with varying degrees of standards, where the most widely used standard was the standard for supporting commitment and senior management, followed by the continuous improvement standard, the measurement standard, the processes and systems standard, the feedback standard, and the human resources standard was the least used standard for the Six Sigma approach. By commercial banks in Palestine, it was recommended that attention be paid to the concept of Six Sigma because of its importance That is, it works to reduce the error rate Working to satisfy customers by providing distinguished banking service and its importance in investment decisions. The commitment of banks operating in the Gaza Strip to the standards of Six Sigma (commitment and support of senior leadership, feedback and measurement, continuous improvement, processes and systems, human resources) to a great extent and the necessity of paying attention to the Six Sigma approach. Emphasizing the possibility of using the approach in banks because of its impact and importance from a scientific standpoint by reducing errors and improving The quality of banking services provided to 133 customers in line with their expectations, and emphasizing the necessity of commitment and support for bank managers to work with the Six Sigma approach because it has a role in the planning process for all stages of auditing and risk assessment (Maher & Heba, 2016). On the contrary, (Hawraa, 2018) discussed the lack of financial support to purchase technologies and programs Sigma in Iraqi private banks, both in terms of the impact of its application Six Sigma aims to improve the quality of banking services, but based on the expectations of senior management, it is optimistic about the required quality (Nehme etal., 2023). Between (Casso et al., 2019) consider the (six sigma) approach a focus of attention for various organizations because of the role it plays in light of the various transformations that have occurred and are occurring in the world of organizations through the contribution of senior management in achieving customer requirements and improving the quality of banking services, and focusing on the necessity of paying attention to this approach and the willingness of banks to apply it to what It is important to ensure its continuity. Based on what was mentioned in previous studies about the advantages that are gained if curriculum standards are applied Six Sigma reduces the rate of errors in operations, especially banking operations, because of their importance in improving the quality of banking service. Most studies have dealt with different sectors in different countries and commercial banks, and no study has touched on the case of Islamic banks - in Iraq. This study is considered a scientific addition (spatial gap) to be addressed. Iraqi Islamic banks. As for the study (Hawraa, 2018), it touched on private commercial banks in Iraq and mentioned the lack of financial support to purchase technologies and programs. Six Sigma, but senior management is optimistic about the required quality. About the current study and based on the results of previous studies that were discussed, it turns out that there is a weakness in the quality of banking service. Accordingly, the opinions of respondents will be analyzed to find out whether the standards of the Six Sigma approach have an impact on improving the quality of banking service if applied.
Six sigma (σ)
In 1987, sigma was only a statistical concept, that is, it is called the standard deviation. Other sectors, represented by finance, development, and human capital, were interested in improving the quality of service by diagnosing irregularities and defects in order to satisfy customers on a large scale. The truth about Six Sigma goes back to the owner of Motorola. Bill Smith in the 1970s in order to improve product quality, that is, the error rate per million operations is 3.4 through standards taken by the facility, and he played a role in warning of quantitative variation in production processes. Thus, Six Sigma was discovered in order to increase efficiency in operational processes to cope with and meet customer needs. (Qureshi et al., 2012). According to the definitions and opinions of various authors about Six Sigma, it is represented by an advanced and wide-ranging methodology that works to create a product of distinguished quality and type, that is, as a road map that begins with collecting data and analyzing it statistically in order to diagnose errors, avoid them, and prevent them from recurring ( Goh, 2002 ). The statistical analytical concept of Six Sigma explains its basic base with a common floor between customers, employees and exporters in order to improve the product and develop the financial performance of the organization through error reduction processes (Abner et al., 2020).
DMAIC process
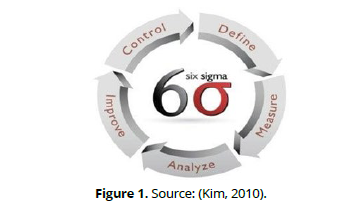
The term Six Sigma model, known as DMAIC, is divided into five stages of the process (Caesaron & Simatupang, 2015). The definition or identification stage is the stage that is used to define the problem or specify customer requirements in order to correct it. Thus, Six Sigma standards work to identify the effective factors that require measurement, analysis, correction and control to achieve financial success using the formulas of the main equations. As for the results of some effective factors, they explain to us the relationship between The result and cause of output processes by measuring them with the inputs that drive the process (Alwan et al., 2023; Alyaseri et al., 2023; Salman et al., 2023). The measurement stage is carried out through quantitative evaluation of certain characteristics or performance levels based on data that can be seen. This process aims to determine the critical quality level that is directly related to customer requirements. Thus, measuring performance has become the size of the sigma value, and every dimension of the service or product must be measured (Saeed et al., 2022). In order to predict the occurrence of violations that hurt the process. The analysis stage represents knowing the main cause of the problem and statistical operations, for Explaining the causal factors and effects resulting from the causal factors, and this is done through the use of a causal diagram (Aditya & Irawan, 2020). The improvement stage represents FMEM, which is a system of activities that works to evaluate the failed situations existing in the organization, especially in the parts of the process, and depends in its work on the factors that affect the process or product. So FMEM represents improving, developing and monitoring the potential failures of inputs and working to reduce the effects resulting from them. failure. It is the control stage that works to determine the effectiveness of many active factors, and aims to continue improvements to the process if it is implemented. Accordingly, the main goal of the control stage, i.e. (monitoring), is to prevent the organization from returning to previous failed operations (Figure 1).
The impact of Six Sigma on the banking sector
There are many studies with experimental results that have been mentioned, the most important of which is a study (Yousefi & Vencheh, 2016) across different scopes to determine the benefits that accrue to organizations by integrating (Six Sigma consensus), (market share and improved profitability), (increasing competitiveness through quality of service and customer 190 satisfaction), and managing, improving and providing human resources. Through cost and packaging reductions there are no defects. Notice (Rod & Gibbs, 2016) that stakeholders, customer satisfaction and loyalty in identifying the brand and the company’s competitive advantage are among the factors that create a desire to upgrade quality through the application of Six Sigma in the banking industry because it contains benefits that cannot be overemphasized in adopting an approach. Six Sigma as a quality management tool, especially in the advanced services sector, is important for expanding operations and business activities, improving and enhancing the quality of financial products and services provided to owners, i.e. it is a strategy of high quality and highly rewarding products/services. There are many advantages to six sigma and its work within banking: Reducing the fees associated with the service provided through high discipline regarding cash distribution, Preparing financial reports by using systems specialized in operational information, Working to reduce the errors associated with credit services of an unproductive nature, Working to reduce the errors associated with collecting commercial papers, Working to reduce errors associated with routine operations and Assisting financial officials in controlling operations by identifying problems, paying attention to customer complaints and reducing them, completing the transaction as quickly as possible, and ensuring proper delivery of the product (Chelangat, 2016). Six sigma education provides an increase in the status and value of shareholders through reducing costs, increasing invested capital, accuracy in delivery, and meeting the needs of customers in financial and non-financial institutions. Thus, six sigma education represents a mixture (six and learn thinking) in order to develop the quality of service and not waste time (Sunder, 2016).
Six Sigma practices in the banking sector
Banking services management has been considered an important matter for several years, and there are initiatives to deal with it through high-quality business process management, such as Six Sigma is taken up by business banking institutions for the development Male (Gulbake & Panga, 2023) that Six Sigma technology is a dynamic business initiative to transform banking operations and has led to increased returns, reduced expenses, and increased revenues. Therefore, it is time to implement this growing phenomenon to gain a competitive advantage in banks and other financial institutions. Six Sigma is being implemented in banking institutions and researchers (Wang & Hussain, 2011) have described it as a tool for maintaining quality and accuracy in cash disbursement to reduce service fees and generate daily reports. Reducing defects in the process like a collection of loans, checks and cash, reducing customer complaints, reducing transaction time, computing, analysis and overall improvement in performance, and as we have observed the significant impact of Six Sigma in the banking industry in India towards improving the banking process in real-time and providing banks with the knowledge of service quality. Provided to clients through performance indicators processing metrics. Thus, it can be said that Six Sigma has been successfully adopted and integrated by banking institutions to enhance their operational processes, businesses, and activities, and the need for Iraqi Islamic banks to benefit from this technology to improve the quality of their services and reduce defects, thus ensuring customer satisfaction and creating satisfactory profitability.
Quality of service
Service quality has a place in the management of institutions of a service nature, especially during the past period (two decades), and any interpretation of the concept of service quality that we observe aims at customer expectations to purchase the service. (Saidani & Saeed, 2023). It explains the service's ability to fulfill the customer's real requirements, and therefore the interpretation of service quality deals with the benefit provided to the customer. (Zimamu and others) It is represented by being one of the important pillars through which institutions can distinguish themselves from each other through the quality of service provided permanently, meaning that it creates a high competitive advantage (Zimamu & Fatima, 2022). Accordingly, the quality of service can be clarified, i.e. the service provided, expected or perceived by customers, and it represents the main criterion for their satisfaction or dissatisfaction, and it is one of the basic items for organizations wishing to develop the quality of their services (Qawagliya & Farid 2013). It is concerned with knowing customers' requirements to implement them and state their expectations about the service provided in order to develop it or address problems. This process of service quality is called (feedback) (Laamour, 2012). The researchers' opinion regarding the definition of service quality is that the organization excels in the quality of its services in order to reach the implementation of customer requirements. Accordingly, the quality of banking service emerged as a path to competitive advantage compared to the services provided by other banks because the vast majority of banks rely on traditional methods in their dealings, and many concepts such as services have become Customers, empathy, speed in implementing requirements, security, and privacy are among the basic concepts to achieve competitive advantage for banks. The term banking service quality is one of the basic terms in providing and marketing services. The main reason for this is that quality represents the main artery for banks' growth through the increase in customer deposits, and thus it is better, to recognise the concept of intangible banking service quality, i.e. the quality of service provided is in accordance with international standards in order to satisfy customers (Mahmoud Shazly, 2022).
Dimensions of banking service quality
Tangibility
Intangible assets include material things and tools of a used nature, in addition to credit cards and quick responses to carrying out transactions. Intangible assets have many positive characteristics, represented by money counters and the external appearance of workers, and they facilitate the overdraft process, working hours, speed and efficiency of transactions i.e. tangible things are as important as empathy. The authors consider it advisable to consider including opening hours of operations within the empathy dimension; Furthermore, the reliability dimension may include overdraft privileges, i.e. viewing tangibles as a distinct element that shows consistency across cultures. (Sultana & Das, 2016) Dependability (reliability): Reliability is the ability of banks to provide services correctly to customers the first time without any error, deliver services at the appropriate time that was agreed upon, and of course distribute various information related to banking through various social media platforms (Solichin et al., 2019). Reliability covers the ability to deliver services exactly what is promised and the ability to be trusted (reliably), especially in providing services promptly, in the same manner, and according to the schedule promised by the bank without any error every time. Reliability means Accuracy in service, provision of service on time, conformity of service implementation, attention to customers and sincerity in service (Kereta,2014).
Response
Responsiveness is an employee's willingness and ability to help customers, respond to what customers want, provide information about when services will be provided, and then provide services immediately. Responsiveness can be called for, including employees' willingness to help and provide services as customers need. If a company ignores consumers' waiting, especially without clear information from the company, this will give a bad impression of where it is located. This should not happen. However, if you respond to errors quickly and responsively, it can become something memorable and an enjoyable experience for consumers or customers (Sitorus, 2009). It represents a deep dimension and includes response variables: clarity of information, speed of service, accuracy of service, desire to help; desire to respond (Kereta, 2014).
Safety
Security perceptions relate to threats that can create conditions, conditions, and events that have the potential to cause economic hardship through data sources or networks being collected, corrupted, data modification, denial of service, fraud, and abuse of authority (Sriwidodo, 2010). At the same time, perceptions of privacy are coupled with the customer's feelings about the banking institution's potential to collect and use data about individuals inappropriately. Rather, credibility allows a specific activity to be carried out after identifying the identity, or there is a guarantee that the identity is only used for certain matters, for example, a website. Without recording transactions (non-repudiation) refers to procedures that protect individuals or organizations from denying that they underwent surgery, indicators in the security and safety variable, including security guarantees, data confidentiality, suitability of work equipment, implementation of work procedures, equipment security (Kinasih, & Albari, 2012).
Empathy
Organizations that make it a priority to provide service are to meet and satisfy customers' needs, and the intent of empathy is that the organization's sole concern for customers and represents the basis of the criteria for empathy is that the customer is important and needs attention, i.e. conveying feelings. And that quantitative study that the service quality model identified dimensions that used security, credibility, and access to measure empathy (Parasuraman et al., 1994).
Hypotheses
H0: There is no statistically significant impact of the Six Sigma curriculum standards and their combined dimensions (senior leadership support, feedback and measurement, continuous improvement, processes and systems, human resources) in improving the quality of banking services in Iraqi Islamic banks at a significance level of 0.05.
H1: There is a statistically significant effect of the Six Sigma curriculum standards and their combined dimensions (senior leadership support, feedback and measurement, continuous improvement, processes and systems, human resources) in improving the quality of banking services in Iraqi Islamic banks at a significance level of 0.05 (Al-Tarawneh, 2020).
H2: There is a direct, statistically significant correlation between the standards of the Six Sigma approach and its combined dimensions (senior leadership support, feedback and measurement, screw-up improvement, processes and systems, human resources) and the quality of banking service at a significance level of 0.05.
Methodology
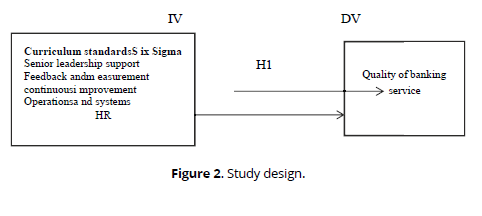
The method used was descriptive and analytical. A quantitative research method was followed to explore the effect of using the standards of the Six Sigma approach in improving the quality of banking service for a sample of Islamic banks operating in Iraq. Most academic studies use the deductive approach to achieve a strong result for the hypothesis that was examined (Trochim, 2001). A random probability sampling technique was used due to the size of the study population to collect data. Respondents were communicated via email using the data collection tool (questionnaire). It was prepared electronically through Google Forms. The questionnaire consists of (48) paragraphs to collect primary data from a sample. The random study consists of three parts: demographic data, (2) Six Sigma standards and their dimensions (the independent variable), and (3) the quality of banking service (the dependent variable). (45) questionnaires were distributed to the study sample, including an official and an employee in the administration and its branches. Relevant (the subject of the study) As for the study population, it consisted of workers in 4 Islamic banks in Iraq, for the period (September - November / 2023), the number of responses from respondents was an average of (39) answers, which were analyzed using the SPSS V.23 statistical program and a number Among the methods and tools are the Cropnagh alpha coefficient for the reliability and validity of the study questions, the fivepoint Likert scale, descriptive analysis (tools for measuring central tendency, statistical dispersion, frequencies, percentages), the multiple linear regression coefficient to show the effect of variables, and quantitative analysis (Pearson correlation coefficient) to show the relationship Correlation between variables (Table 1, Figure 2, Table 2).
| Variables | Elements | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Senior leadership support | 5 | (Yassin et al., 2021) |
| Feedback and measurement | 5 | ( Al-tarawih, 2019) |
| continuous improvement | 8 | (Singh & Singh, 2015) |
| Operations and systems | 5 | (Ghaleb & Abdulhad, 2022) |
| HR | 5 | (Krueger & Adams, 2014) |
| Quality of banking service | 20 | (Al-Omari& Hani, 2011) |
| variable | class | Repetition | percentage % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | male | 25 | 64.1 |
| female | 14 | 35.9 | |
| Academic achievement | Preparatory school | 4 | 10.2 |
| Bachelor's | 29 | 74.4 | |
| Years of Experience | Postgraduate | 6 | 15.4 |
| less than 5 | 1 | 2.6 | |
| 5-10 year | 21 | 53.8 | |
| 10-20 year | 12 | 30.8 | |
| More than 20 | 5 | 12.8 | |
| 20-30 | 2 | 5.1 | |
| Age | 31-40 | 25 | 64.1 |
| 41-50 | 10 | 25.7 | |
| More than 50 | 2 | 5.1 | |
| employee | 15 | 38.5 | |
| Career Level | Division manager | 18 | 46.2 |
| Director of the Department | 6 | 15.3 | |
| Total | 39 | 100 |
The above table shows that approx. 1.64% of the respondents are male, which indicates that there is a higher level of influence of men's opinions on our results. The reason behind the high percentage of males is due to the majority of banking sector employees in Iraq are male. The table above shows that half of the survey participants are from this age group H31-40 in a rate of 1.64% and class 41-50 in a rate of 25.7 % for the rest of the age groups 20-30, more than 50 in the rate of 5.1% the reason is due to the demographic composition of Iraqi society, the youth group. The above table shows that 74.4% of the sample members had done so, that is, they had completed their bachelor’s degree and postgraduate studies at the rate of 15.4% and preparatory school 10.2% this shows that most of the employees hold a good certificate, that is, specialists. The table above shows that most of the respondents have had a job service from 5-10 years a percentage of half the total percentage of respondents, i.e. a percentage 53.8%. There is diversity in the number of respondents concerning their job titles, and this indicates that there are officials for all job positions to participate in an initiative that works to improve the quality of services and revitalize the banking sectors in Iraq, and they have the highest percentage. 46.2% Division managers and employees 38.5% and department managers 15.3%.
Reliability statistic
(Table 3)
| Cronbach's Alpha | N of Items |
|---|---|
| 0.814 | 48 |
We can see from the above information that the stability coefficient Cronbach's Alpha They were all with a good degree of reliability (consistency) for all variables and they were all above the conditional level of 0.60 according to Uma-Sekaran (2003). The overall reliability of the questionnaire was 0.814%, which is a high percentage of reliability
Reliability statistics
(Tables 4, 5)
| Variables | Cronbach's Alpha | N of Items |
|---|---|---|
| Senior leadership support | 0.791 | 5 |
| Feedback and measurement | 0.791 | 5 |
| continuous improvement | 0.723 | 8 |
| Operations and systems | 0.772 | 5 |
| HR | 0.786 | 5 |
| Quality of banking service | 0.87 | 20 |
| Variables | Mean | Std. Deviation | N |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quality of banking service | 79.7692 | 8.77035 | 39 |
| Senior leadership support | 19.5128 | 2.57387 | 39 |
| Feedback and measurement | 19.8462 | 2.31174 | 39 |
| continuous improvement | 30.7949 | 4.87302 | 39 |
| Operations and systems | 19.5128 | 2.57387 | 39 |
| HR | 19.6923 | 2.36369 | 39 |
Based on the results of the descriptive analysis of the independent variable (dimensions of curriculum standards Six Sigma), the dependent variable (banking service quality), and the use of measures of central tendency and statistical dispersion show that After continuous improvement of curriculum standards Six sigma With the highest arithmetic average (30.7949) and the standard deviation (4.87302) In improving the quality of banking service represented by (tangibility, dependability, reliability, responsiveness, safety, empathy) through the bank’s management considering that continuous improvement is part of the requirements for the quality of banking service and working to control quality, know customer suggestions, and work to train 378 department heads by forming work teams. For reducing deviations and errors that occur in the service development, process and accuracy in detecting errors in the banking services provided.
Testing the study hypotheses
H0: There is no statistically significant impact of the Six Sigma curriculum standards and their combined dimensions (senior leadership support, feedback and measurement, continuous improvement, processes and systems, and human resources) in improving the quality of banking services in Iraqi Islamic banks at a significance level of 0.05.
H1: There is a statistically significant effect of the Six Sigma curriculum standards and their combined dimensions (senior leadership support, feedback and measurement, continuous improvement, processes and systems, human resources) in improving the quality of banking services in Iraqi Islamic banks at a significance level of 0.05.
H2: There is a positive, statistically significant correlation between the standards of the Six Sigma approach and its combined dimensions (senior leadership support, feedback and measurement, continuous improvement, processes and systems, human resources) and the quality of banking service at a significance level of 0.05 (Table 6).
| Correlations | Quality of banking service |
Senior leadership support |
Feedback and measurement | continuous improvement | Operations and systems | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | ||||||
| Quality of banking service | 1 | 0.461 | 0.567 | 0.671 | 0.643 | 0.552 |
| Senior leadership support | 0.461 | 1 | 0.451 | 0.632 | 0.635 | 0.727 |
| Feedback and measurement | 0.567 | 0.451 | 1 | 0.679 | 0.637 | 0.482 |
| continuous improvement | 0.671 | 0.632 | 0.679 | 1 | 0.781 | 0.705 |
| Operations and systems | 0.643 | 0.635 | 0.637 | 0.781 | 1 | 0.598 |
| HR | 0.552 | 0.727 | 0.482 | 0.705 | 0.598 | 1 |
| Quality of banking service | . | 0.002 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Senior leadership support | 0.002 | . | 0.002 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Feedback and measurement | 0 | 0.002 | . | 0 | 0 | 0.001 |
| continuous improvement | 0 | 0 | 0 | . | 0 | 0 |
| Operations and systems | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | . | 0 |
| HR | 0 | 0 | 0.001 | 0 | 0 | . |
Correlations
The correlation is considered weak if the correlation coefficient is...0.01-0.49 and can be considered average if the value of the correlation coefficient ranges between 0.50-0.69. If the correlation coefficient is between 0.70-0.99, the relationship is seen as a strong correlation between the two variables and + 1 represents a perfect correlation. Through the coefficient table, Cronbach's Alpha the questionnaire items are valid and internally consistent. Because the overall reliability of the questionnaire questions is 0.814%, which is more than 0.60% (uma-sekaran, 2003). It was shown from the correlation analysis table Correlations are the correlational relationships between the independent variable, the standards of the Six Sigma approach and its dimensions (senior leadership support, feedback and measurement, continuous improvement, processes and systems, human resources) and the dependent variable (quality of banking service), where the Pearson Correlation coefficient represents a positive direct correlation relationship at a significance level of 0.05 because The Sig for all dimensions of the independent variable is less than the significance level of 0.05, and the correlation between the dimensions of the independent variable among them, as the Pearson Correlation coefficient represents a positive direct correlation at the significance level of 0.05 because the Sig for all dimensions is less than the significance level of 0.05. Therefore, we accept hypothesis H2.
Variables Entered/Removed
(Table 7)
| Model | Variables Entered | Variables Removed | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HR Feedback and measurement, processes and systems, senior leadership support, continuous improvement b | 0 | Enter |
Model Summery
(Table 8)
| Model | R | R Square | Adjusted R Square | Std. Error of the Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.715a | 0.511 | 0.437 | 6.58098 |
Based on the outputs of multiple linear regression and a table Model Summary, where (R 0.715) represents the presence of a 419 direct correlation between the dependent and independent variables, while the variance of the joint prediction of the independent variable (the standards of the Six Sigma approach and its dimensions) affects by an amount of (R2 Square 51%) on the dependent variable (quality of banking service) Therefore, we accept hypothesis H1 and reject hypothesis H0ANOVA (Table 9).
| Model | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Regression | 1493.72 | 5 | 298.743 | 6.898 | 0.000b |
| Residential | 1429.21 | 33 | 43.309 | |||
| Total | 2922.92 | 38 |
The table shows ANOVA a analysis of variance supports the value F (6.898) is statistically significant because the sig of 0.000 is less than the significance level of 0.05. Therefore, the relationship model is multiple linear and has good quality, and the results can be relied upon.
Coefficients
(Table 10)
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients |
Correlations | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t | Sig. | |||||||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | Zero-order | Partial | Part | |||
| (Constant) | 27.091 | 11.292 | 2.399 | 0.022 | ||||
| Senior leadership support | -.323- | 0.649 | -.095- | -.498- | 0.622 | 0.461 | -.086- | -.061- |
| Feedback and | 0.586 | 0.647 | 0.154 | 0.905 | 0.372 | 0.567 | 0.156 | 0.11 |
| measurement | ||||||||
| continuous | 0.504 | 0.425 | 0.28 | 1.187 | 0.244 | 0.671 | 0.202 | 0.145 |
| improvement | ||||||||
| Operations and systems | 0.939 | 0.714 | 0.276 | 1.315 | 0.198 | 0.643 | 0.223 | 0.16 |
| HR | 0.685 | 0.743 | 0.185 | 0.923 | 0.363 | 0.552 | 0.159 | 0.112 |
The table shows Coefficientsa the relationship between the Pearson correlation coefficient and multiple linear regression, to show the significant effect Curriculum standards Six Sigma in its dimensions (the independent variable) on the dependent variable (quality of banking service) and because all dimensions are at the significance level of 0.05 because the significance of the sig for all the independent dimensions is less than the significance level of 0.05. This means that the two independent dimensions (continuous improvement, processes and systems) have a fundamental impact on the variable. The dependent dimension (the quality of banking service), while the rest of the independent dimensions represent a fundamental influence and a correlational relationship between them only (Figure 3).
Conclusions and Recommendations
Conclusions
Iraqi banks suffer from many problems and variables due to the nature of the environmental conditions and the privacy in which they carry out their activities. The use of traditional methods in Iraqi banks and the failure to switch to electronic banking techniques led to a lack of customers and a decrease in the customer base. Through statistical analysis, it was found that there is a direct (positive) correlation between curriculum standards Six Sigma with its combined dimensions (senior leadership support, feedback and measurement, continuous improvement, processes and systems, human resources) and the quality of banking service in Iraqi Islamic banks. Through the statistical analysis, it was found that the criteria have a method Six Sigma Its combined dimensions (senior leadership support, feedback and measurement, continuous improvement, processes and systems, human resources) affect an amount 51% In improving the quality of banking services in Iraqi Islamic banks. Through statistical analysis, it was found that the two independent dimensions (continuous improvement, processes and systems) have a fundamental impact on the dependent variable (banking service quality).
Recommendations
Encouraging banks to use financial analysis as a method of control, through the use of financial indicators, financial ratios and standards assigned to them, to quickly detect errors and deviations, and for the institution to achieve its goals about customer satisfaction. Develop and enhance security procedures to protect customer accounts and personal information by providing additional verification technologies such as facial and fingerprint recognition to increase security. Using modern methods and technologies by developing the user interface for the banking application and the website to make it easier to use and interact with customers and providing customization tools that allow them to adjust the interface and personalize their experience. Working on training and developing employees through workshops to ensure that they are familiar with all aspects of banking services and encouraging them to provide distinguished and exceptional customer service that meets their future needs and requirements.
Scientific contribution to the study
This study contributed to analyzing and improving marketing processes, thus increasing the effectiveness of sales quality and achieving growth goals, and also reducing risks through verification procedures and enhancing the robustness of systems in Islamic banks in Iraq, and as a result enabling them to increase their customer base.
References
Abass, Z. K., Al-Abedi, T. K., & Flayyih, H. H. (2023). INTEGRATION BETWEEN COBIT AND COSO FOR INTERNAL CONTROL AND ITS REFLECTION ON AUDITING RISK WITH CORPORATE GOVERNANCE AS THE MEDIATING VARIABLE. International Journal of Economics and Finance Studies, 15(2), 40–58. https://doi.org/10.34109/ijefs.202315203
Abdulzahra, A. N., Al-Shiblawi, G. A. K., Flayyih, H. H., Elaigwu, M., Abdulmalik, S. O., Talab, H. R., & Audu, F. (2023). Corporate Governance Towards Sustainability Performance Quality: A Case of Listed Firms in Malaysia. Journal of Information Systems Engineering and Management, 8(4). https://doi.org/10.55267/iadt.07.14051
Abner, I. P., Idamoyibo, H. R., Jack, A. E., Ndubuaku, V., & Samuel, U. E. (2020). Six-Sigma Model and the Growth of the Banking Sector in Nigeria. International Journal of Management (IJM), 11(11). DOI: 10.34218/IJM.11.11.2020.079
Aditya, G. M., & Irawan, H. (2020). Application Of the Six Sigma Method As A Tool For Management To Improve Quality Of Services (case Study On Bank
BNI Syariah Bandung). eProceedings of Management, 7(1) file:///C:/Users/ok/Downloads/11472-22334-1-SM%20(6).pdf
Alabboodi, A. S. (2019). The effect of customer satisfaction on service quality: The case of Iraqi banks. International Journal of Applied Research, 5(1), 146-152. http://www.allresearchjournal.com/
Ali, S. I., Al-taie, B. F. K., & Flayyih, H. H. (2023). THE EFFECTS OF NEGATIVE AUDIT AND AUDIT ENVIRONMENT ON THE INTERNAL AUDITOR PERFORMANCE: MEDIATING ROLE OF AUDITING PROCESS INDEPENDENCE. International Journal of Economics and Finance Studies, 15(1), 64–79. https://doi.org/10.34109/ijefs.202315105
Al-Omari, & Hani Abdel Rahman Omar. (2011). The extent of compliance with international quality accreditation standards in the health services sector in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. An exploratory study was applied to the Jeddah Governorate. Arab Journal of Administration, 31(2).
Al-Rubaye, M. M. M. (2020). The influence of regulatory commitment on the quality of banking service: an empirical study on trade banks in Iraq. Polish Journal of Management Studies, 22(2), 22-35. DOI: 10.17512/pjms.2020.22.2.02
Al-tarawneh, R. M. (2019). The effect of using the six sigma approach in improving the quality of health services in the Jordanian Ministry of Health. International Business Research, 12(12), 11-28. https://doi.org/10.5539/ibr.v12n12p11
Alwan, S. A., Jawad, K. K., Alyaseri, N. H. A., Subhi, K. A., Hussein, E. K., Aned, A. M., Sharaf, H. K., Flayyih, H. H., Salman, M. D., Abdulrasool, T. S., Abdulrasool, T. S., & Abed, R. A. (2023). THE PSYCHOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF PERFECTIONISM ON SPORT, ECONOMIC AND ENGINEERING STUDENTS. Revista Iberoamericana de Psicologia Del Ejercicio y El Deporte, 18(3), 330–333. https://www.riped-online.com/archive/riped-volume-18-issue-3-year-2023.html
Alyaseri, N. H. A., Salman, M. D., Maseer, R. W., Hussein, E. K., Subhi, K. A., Alwan, S. A., zwaid, J. G., Aned, A. M., Jawad, K. K., Flayyih, H. H., Bachache, N. K., & Abed, R. A. (2023). EXPLORING THE MODELING OF SOCIO- TECHNICAL SYSTEMS IN THE FIELDS OF SPORT, ENGINEERING AND ECONOMICS. Revista Iberoamericana de Psicologia Del Ejercicio y El Deporte, 18(3), 338–341.
Antony, J., & Banuelas, R. (2002). Key ingredients for the effective implementation of Six Sigma program. Measuring business excellence, 6(4), 20-27. https://doi.org/10.1108/13683040210451679
Ayser Hassan Ismail. (2022). The Quality of Banking Service Effect in Organizational Integration Expiratory. (Study in several Iraqi Banks). ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL SCIENCES JOURNAL, (Special Issue) https://www.iasj.net/iasj/download/4b5562acc2387444
Basri, D. A. R. S., & Taher, H. A. (2018). Electronic banking techniques and their impact on the quality of banking service comparative study of some branches of Iraqi government and private banks. Journal of Administration and Economics, (114).
https://www.iasj.net/iasj/download/2579180b1156a5d0
Bofas Al-Sharif. (2013) Total quality management and change in the economic institution (Doctoral dissertation, University of Badji Mokhtar Annaba, Sidi Ashour.)
Bonnie, & Naima (2016). Study of the possibility of applying the Six Sigma approach to improve the quality of banking services - a case study of Badr Bank, M’sila Agency (Doctoral dissertation), University of M’sila. http://dspace.univ- msila.dz:8080//xmlui/handle/123456789/9909
Bushra Hashem Muhammad Al-Azzawi, & Ayser Hassan Ismail. (2017). Mackenzie's role model dimensions in the quality of service," a Prospective study of the views of a sample of Iraqi bank managers. Journal of Economics and Administrative Sciences, 23(99). https://doi.org/10.33095/jeas.v23i99.247
Caesaron, D., & Simatupang, S. Y. P. (2015). Implementasi pendekatan DMAIC untuk perbaikan proses produksi pipa PVC (studi kasus PT. Rusli Vinilon). Jurnal Metris, 16(02), 91-96.
Chakrabarty, A., & Chuan Tan, K. (2007). The current state of six sigma application in services. Managing service quality: An international journal, 17(2), 194-208. https://doi.org/10.1108/09604520710735191
Chelangat, B. (2016). The Extent of Implementation of Lean Six Sigma within Commercial Banks in Kenya. IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSR-JBM), 18(12), 31-37. DOI: 10.9790/487X-1812023137
Cheng, J. L. (2008). Implementing Six Sigma via TQM improvement: an empirical study in Taiwan. The TQM Journal, 20(3), 182-195. http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/17542730810867218
Dinell, D. (2003). Banking goes Six Sigma. Wichita Business Journal, November, 21.
Elias, H. S., & Azhar, N. M. (2019). Effects of customer service quality dimension on customer satisfaction in Iraqi Banking Sector. World Wide Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Development, 5(7), 21-28.
Flayyih, H. H., & Khiari, W. (2023). Empirically Measuring the Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility on Earnings Management in Listed Banks of the Iraqi Stock Exchange: The Mediating Role of Corporate Governance. Industrial Engineering and Management Systems, 22(3), 273–286. https://doi.org/10.7232/iems.2023.22.3.273.
Garrison, R. H., Noreen, E. W., Brewer, P. C., & McGowan, A. (2010). Managerial accounting. Issues in Accounting Education, 25(4), 792-793. https://doi.org/10.2308/iace.2010.25.4.792
Ghaleb, G. S., & Abdulahad, A. F. (2022). The Improving of Internal Auditing Quality Performance by the Use of Six Sigma Methodology Standards: An Applied Study Conducted at the General Company for Ports of Iraq. resmilitaris, 12(2), 5398-
5412.
Goh, T. N. (2002). A strategic assessment of Six Sigma. Quality and Reliability Engineering International, 18(5), 403-410. https://doi.org/10.1002/qre.491
Gulbake, P., & Panga, M. (2023). Exploring Six Sigma Practices, Critical Success Factors and Business Performance in the Indian Banking Sector. EuropeanEconomic Letters (EEL), 13(3), 1473-1489. https://www.eelet.org.uk/index.php/journal/article/view/451/385
Hammam, A. Y. s., & Ashraf Youssef Selim. (2012). Using the Six Sigma methodology to improve the quality of service performance: an applied study on the health services sector in Taif. Trade and Finance, 32(4), 191-232.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21608/caf.2012.130048
Harry, M. J., & Schroeder, R. (1999). Six sigma, the breakthrough management strategy revolutionizing. The World’s Top Corporations. Bantam Doubleday Dell, New York. http://dx.doi.org/10.1198/tech 2001.s622
Hassan Mohammed Yassin, A., Elzein Abukassawi Osman, N., Abedelmonem Ben Khalifa, W., & Nouh Mohammed Adam, E. (2021). An Application for Measuring and Analyzing the Level of Performance Accuracy for Health Services Quality Indicators by Using Six-Sigma: A Study Case of Government Hospitals in Khartoum State. Journal of Healthcare Engineering, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8425206
Hassoun, H. I., & Khalaf, P. D. W. J. (2022). Dimensions of banking service quality in Iraqi commercial and Islamic banks (a comparative study). Journal of Administration and Economics, 1(133). https://bcuj.baghdadcollege.edu.iq/index.php/BCESUJ/article/view/236
Hawra Ihsan Khalil. (2018). The extent to which Six Sigma concepts can be applied in evaluating and improving the level of performance - applied research in a sample of Iraqi private banks in Najaf Al-Ashraf, Journal of Kufa Studies Center, 1(49) https://doi.org/10.36322/jksc.v1i49.5051
Hensley, R. L., & Dobie, K. (2005). Assessing readiness for six sigma in a service setting. Managing Service Quality: An International Journal, 15(1), 82-101. https://doi.org/10.1108/09604520510575281
Kasu, Malas, Osmaniye, Hutiya, & age/framed. (2019). The impact of using the Six Sigma approach in improving the performance of commercial banks (Doctoral dissertation), Ahmed Deraya University Adrar. https://dspace.univ- adrar.edu.dz/jspui/handle/123456789/3235
Kateh, Z. H., & Muhaisen, S. R. (2022). The impact of comprehensive banking on the quality of banking services from the customer's point of view A survey of the Middle East Bank of Iraq for investment. Baghdad College of Economic Sciences University Journal (BCESUJ), 75-92.
Kereta, L. B. (2014). Analisis Pengaruh Kualitas Pelayanan Terhadap Kepuasan Pelanggan Pada Perusahaan Daerah Air Minum (PDAM) Kabupaten FloresTimur. Jurnal Administrasi Publik dan Birokrasi, 1(3), 72463. http://repository.ut.ac.id/id/eprint/951
Khaled Ahmed Ibrahim Al-Qassas. (2014) (Using the Six Sigma approach to rationalize investment decision-making: an applied study on Palestinian commercial banks) (Doctoral dissertation, Batch2). http://dspace.alazhar.edu.ps/xmlui/handle/123456789/2472
Kim, D. S. (2010). Eliciting success factors of applying Six Sigma in an academic library: A case study. Performance Measurement and Metrics, 11(1), 25-38. https://doi.org/10.1108/14678041011026847
Kinasih, B. S., & Albari, A. (2012). Pengaruh persepsi keamanan dan privasi terhadap kepuasan dan kepercayaan konsumen online. Jurnal Siasat Bisnis, 16(1). https://doi.org/10.20885/jsb.vol16.iss1.art3
Knowles, G. (2011). Six sigma. Bookboon. https://my.uopeople.edu/pluginfile.php/57436/mod_book/chapter/39150/BUS4406.QM2.pdf
Kowalik, K. (2018). Six Sigma is a method of improving the quality of the service process. Production Engineering Archives, 19(19), 10-15. https://doi.org/10.30657/pea.2018.19.03
Krishnan, B. R., & Prasath, K. A. (2013). Six Sigma concept and DMAIC implementation. International Journal of Business, Management & Research (IJBMR), 3(2), 111-114.
Krueger, D. C., Mellat Parast, M., & Adams, S. (2014). Six Sigma implementation: a qualitative case study using grounded theory. Production Planning & Control, 25(10), 873-889. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2013.771414
Kumar, M., Antony, J., Madu, C. N., Montgomery, D. C., & Park, S. H. (2008). Common myths of Six Sigma demystified. International journal of quality & reliability management 25(8),878-895. http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/02656710810898658
Laamour Rmeila. (2012). Fundamentals of total quality management in service organizations between theory and practice. Al- Wahat Journal for Research and Studies, 5(2). https://www.asjp.cerist.dz/en/downArticle/2/5/2/136781
Lee, K. C., & Choi, B. (2006). Six Sigma management activities and their influence on corporate competitiveness. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 17(7), 893-911. https://doi.org/10.1080/14783360600595351
Maher Musa Dergham, & Heba Mahmoud Abdullah. (2016). The extent of commitment to the Six Sigma approach in controlling the quality of internal auditing (an applied study on banks operating in the Gaza Strip). Journal of the Islamic University for Economic and Administrative Studies. 21(2). file:///C:/Users/ok/Downloads/370-1144-1-PB.pdf
Mahmoud Shazly, A. (2022). The effect of perceived fairness on customer retention. Egyptian Journal of Business Studies, 46(3), 351-400. https://dx.doi.org/10.21608/alat.2022.260741
Maseer, R. W., Zghair, N. G., & Flayyih, H. H. (2022). RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN COST REDUCTION AND REEVALUATING CUSTOMERS’ DESIRES: THE MEDIATING ROLE OF SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT. International Journal of Economics and Finance Studies, 14(4), 330–344. https://doi.org/10.34109/ijefs.20220116
Nehme, A. A., Hasan, A. M., Al-Janabi, A. S. H., Al-Shiblawi, G. A. K., Salman, M. D., Hadi, H. A., Hasan, M. F., Al-Taie, A. H. H., Al-taie, B. F. K., Ali, S. I., Zghair, N. G., Maseer, R. W., Flayyih, H. H., Hussein, M. K., Al-Saedi, A. H., Al- Ibraheemi, S. A. R. A. A., & Jawad, K. K. (2023). THE IMPACT OF COVID-19 ON FOOTBALL CLUB STOCK INTEGRATION AND PORTFOLIO DIVERSIFICATION. Revista Iberoamericana de Psicologia Del Ejercicio y El Deporte,15(5), 562–567.
Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V. A., & Berry, L. L. (1994). Reassessment of expectations as a comparison standard in 607 measuring service quality: implications for further research. Journal of Marketing, 58(1), 111-124. 608 https://doi.org/10.1177/002224299405800109
Qawajliyya, Khamili, & unique. (2013). The role of total quality management in improving the performance of an economic institution. http://hdl.handle.net/123456789/1003
Qureshi, M. I., Bashir, N., Zaman, K., Sajjad, N., & Fakhr, S. (2012). Customer Satisfaction Measurement and Analysis using six sigma in the Telecom sector of Pakistan. European Journal of Sustainable Development, 1(1), 53.
http://www.ecsdev.org/web/images/V1I1/volume%201%20issue%201%204.pdf
Rod, M., Ashill, N. J., & Gibbs, T. (2016). Customer perceptions of frontline employee service delivery: A study of Russian 615 bank customer satisfaction and behavioural intentions. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 30, 212-221. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2016.02.005
Saeed, H. S., Hasan, S. I., Nikkeh, N. S., & Flayyih, H. H. (2022). The mediating role of sustainable development in the 618 relationship between producer cost expectations and customer desires. Journal of Sustainability Science and Management, 619 17(10), 13–21.
Saidani, & happy. (2023). Lectures on services marketing. http://dspace.univ-tiaret.dz/bitstream/123456789/9681/1/mark-Serv-saidani-s.pdf
Salaheldin, S. I., & Abdelwahab, I. S. (2009). Six Sigma practices in the banking sector in Qatar. Global Business and Management Research: An International Journal, 1(1), 23-35. file:///C:/Users/ok/Downloads/SixSIgmainBank2009%20(7).pdf
Salman, M. D., Alwan, S. A., Alyaseri, N. H. A., Subhi, K. A., Hussein, E. K., Sharaf, H. K., Bachache, N. K., Jawad, K. K., Flayyih, H. H., Abed, R. A., zwaid, J. G., & Abdulrasool, T. S. (2023). THE IMPACT OF ENGINEERING ANXIETY ON
STUDENTS: A COMPREHENSIVE STUDY IN THE FIELDS OF SPORT, ECONOMICS, AND TEACHING METHODS. Revista Iberoamericana de Psicologia Del Ejercicio y El Deporte, 18(3), 326–https://www.riped-online.com/archive/riped-volume-18-issue-3-year-2023.html
Singh, J., & Singh, H. (2015). Continuous improvement philosophy–literature review and directions. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 22(1), 75-119. https://doi.org/10.1108/BIJ-06-2012-0038
Sitorus, M. (2009). Pengaruh reliability, responsiveness, assurance, empathy dan tangibles terhadap kualitas pelayanan publik 633 (studi kasus kantor pelayanan terpadu kota dumai). Jurnal Borneo Administrator, 5(1). https://doi.org/10.24258/jba.v5i1.40 634
Solichin, M., Rasyidi, R., & Halimatusa’diah, S. (2019). Pengaruh Kualitas Pelayanan (Reliability, Assurance, Tangible, 635 Empathy, Dan Responsiveness) terhadap Kepuasan Nasabah pada Bank Kalteng Cabang Muara Teweh. Jurnal Bisnis dan Pembangunan, 8(2), 38-http://dx.doi.org/10.20527/jbp.v8i2.7918
Sriwidodo, U., & Indriastuti, R. T. (2010). Pengaruh dimensi kualitas pelayanan jasa terhadap kepuasan nasabah. Jurnal Ekonomi dan Kewirausahaan, 10(2). https://ejurnal.unisri.ac.id/index.php/Ekonomi/article/view/363/323
Stoiljkovic, V., Milosavljevic, P., & Randjelovic, S. (2010). Six Sigma concept within the banking system. African Journal of Business Management, 4(8), 1480. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJBM.9000509
Sultana, S., & Das, T. I. S. (2016). Measuring customer satisfaction through SERVQUAL model: A study on beauty parlours in Chittagong. European Journal of Business and Management, 8(35), 97-108.
Sunder M, V. (2016). Reject reduction in a retail bank using Lean Six Sigma. Production Planning & Control, 27(14), 1131- 1142. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2016.1187312
Tarawneh, Ramzi Mubarak (2020). The effect of using the Six Sigma approach (SIX SIGMA) in improving the quality of health services in the Jordanian Ministry of Health, Jordan.
Trochim, W. M., & Donnelly, J. P. (2001). Research methods knowledge base (Vol. 2). Macmillan Publishing Company, New York: Atomic Dog Pub..
Uluskan, M. (2016). A comprehensive insight into the Six Sigma DMAIC toolbox. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma, 7(4), 406-429. DOI: 10.1108/IJLSS-10-2015-0040
Uprety, I. (2009). Six Sigma in banking services: a case study based approach. International Journal of Six Sigma and Competitive Advantage, 5(3), 251-271. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJSSCA.2009.028096
Wang, L., & Hussain, I. (2011). Banking sector growth in China: can Six-Sigma be a solution? International Journal of Business and Management, 6(2), 169. http://dx.doi.org/10.5539/ijbm.v6n2p169
Yang, Z., Peterson, R. T., & Huang, L. (2001). Taking the pulse of Internet pharmacies. Marketing Health Services, 21(2), 4-10.
Yousefi, A., & Hadi-Vencheh, A. (2016). Selecting six sigma projects: MCDM or DEA? Journal of Modelling in Management, 11(1), 309-325. http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/JM2-05-2014-0036
Zhuo, Z. (2019). Research on using Six Sigma management to improve bank customer satisfaction. International Journal of Quality Innovation, 5(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40887-019-0028-6
zimamu, eiqab, & Fatima. (2022.) The role of quality management in supporting the quality of services to achieve customer 662 loyalty - a case study at Algeria Telecom Corporation, Tiaret Branch 2021/2022 (Doctoral dissertation), Ibn Khaldun 663 University - Tiaret. file:///C:/Users/ok/Downloads/TH.M.COM.AR.2022.128.pdf